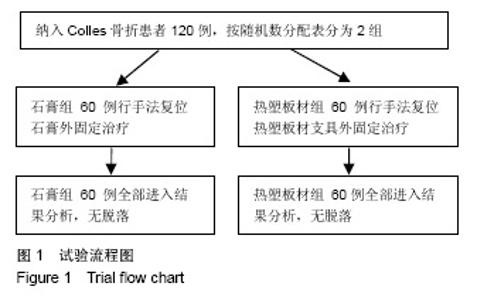
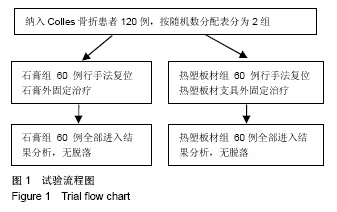
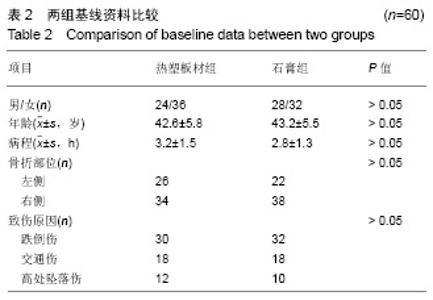
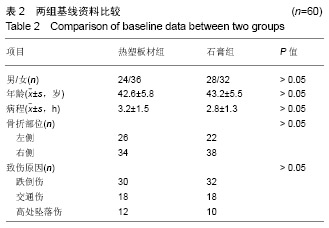
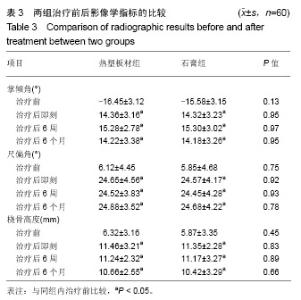
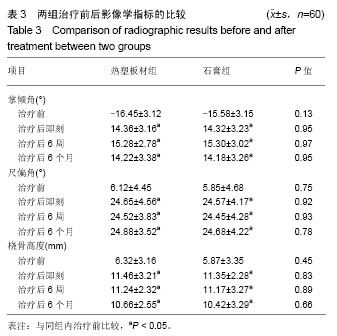
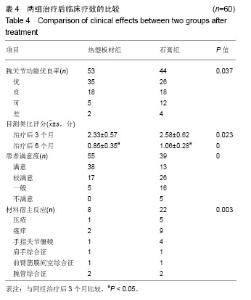
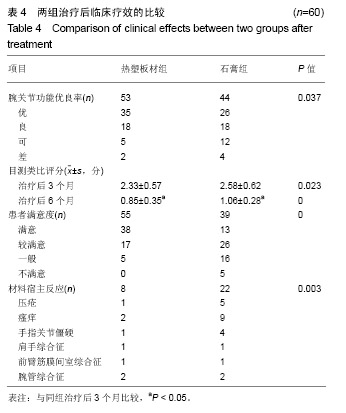
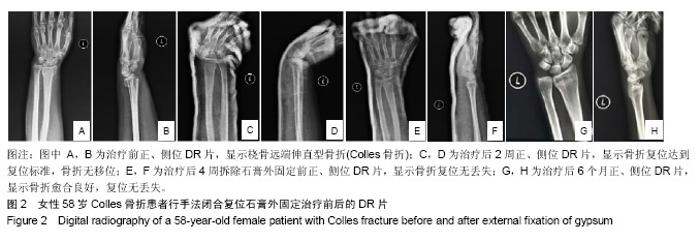
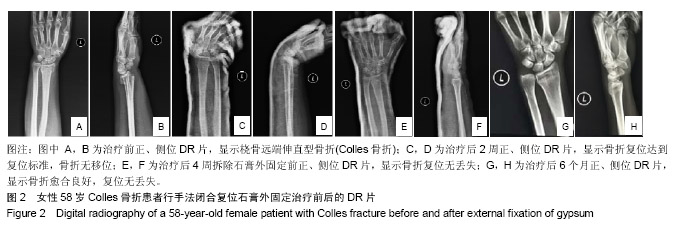
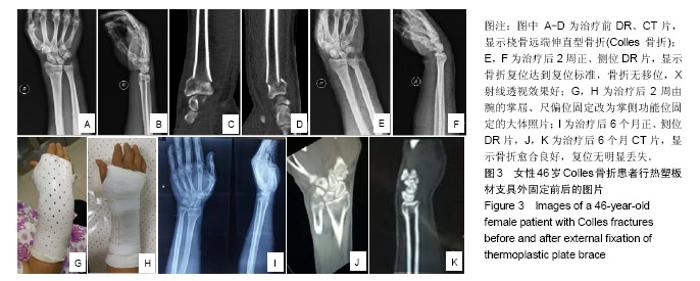
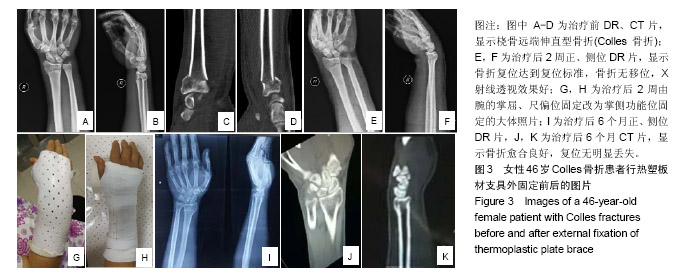
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (22): 3469-3474.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1752
Previous Articles Next Articles
External fixation of thermoplastic plate brace versus gypsum for treating Colles fracture: a randomized controlled trial
- Department of Orthopedics, Central South University Xiangya School of Medicine Affiliated Haikou Hospital, Haikou 570208, Hainan Province, China
-
Received:2019-03-06Online:2019-08-08Published:2021-04-28 -
Contact:Wu Duoqing, Associate chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Central South University Xiangya School of Medicine Affiliated Haikou Hospital, Haikou 570208, Hainan Province, China -
About author:Kong Changgeng, Master, Attending physician, Department of Orthopedics, Central South University Xiangya School of Medicine Affiliated Haikou Hospital, Haikou 570208, Hainan Province, China -
Supported by:the Natural Science Foundation of Hainan Province, No. 814379 (to WCR); the Major Science and Technology Program of Haikou, No. 2014-081 (to KCG)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Kong Changgeng, Wu Duoqing, Fu Linxiong, Huang Youhua, Wang Congren. External fixation of thermoplastic plate brace versus gypsum for treating Colles fracture: a randomized controlled trial[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(22): 3469-3474.
share this article
| [1]殷兵,王娟,赵海涛,等.2003-2012年河北医科大学第三医院Colles骨折的流行病学研究[J].中华创伤手外科杂志, 2014,16(10):873-876.[2]刘勃,李佳,李石,等.2010年至2011年中国东部和西部地区Colles骨折的流行病学对比分析[J].中华创伤骨科杂志, 2017,19(10):892-896.[3]Cooney WP 3rd,Dobyns JH,Linscheid RL.Complications of Colles’ fractures.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1980;62(4):613-619.[4]Baruah RK,Islam M,Haque R.Immobilisation of extra-articular distal radius fractures (Colles type) in dorsiflexion.The functional and anatomical outcome.J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2015;6(3):167-172. [5]郑勇.小夹板及石膏外固定治疗Colles骨折疗效的系统评价[J].四川解剖学杂志,2017,25(3):1-4.[6]唐列,胡晓东,贾秋良.闭合性Colles骨折手法复位麻醉方式的选择[J].深圳中西医结合杂志,2016,26(4):14-17.[7]殷浩,潘政军,陈光,等.手法复位低温热塑支具外固定治疗桡骨远端骨折临床观察[J].中国中医急症,2015,24(3):538-540.[8]李自强,程丽莎,浦创,等.康复干预对非手术Colles骨折后功能的影响[J].中国当代医药,2014,21(34):184-185,190.[9]Christersson A,Larsson S,Östlund B,et al.Radiographic results after plaster cast fixation for 10 days versus 1 month in reduced distal radius fractures: a prospective randomised study.J Orthop Surg Res.2016; 11(1):145.[10]Lee CH,Lee TY,Her JS,et al.Single-Blinded, Randomized Preliminary Study Evaluating the Effect of Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation on Postoperative Pain in Patients with Colles’ Fracture.J Altern Complement Med. 2015;21(12):754-758.[11]Gartland JJ Jr,Werley CW.Evaluation of healed Colles’s fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am.1951; 33(4):895-907.[12]Liang B,Lai JM,Murugan A,et al.Proposed Guidelines for Treatment of Concomitant DistalRadius and Distal Ulna Fractures.Hand Surg. 2015; 20(3):396-401.[13]Kani KLK,Mulcahy H,Chew FS.Understanding carpal instability:a radiographc perspective.Skeletal Radiol. 2016;45(8):1031-1043.[14]方媛,蒋定尧,龚向阳,等.X线分型对老年人Colles骨折治疗策略及预后的价值研究[J].临床放射学杂志, 2016,35(10):1560-1565.[15]Grewal R,Perey B,Wilmink M,et al.A randomized prospectivestudy on the treatment of intra?articular distal radius fractures:open reduction and internal fixation with dorsal plating versusmini open reduction, percutaneous fixation, and external fixation.J Hand Surg Am. 2005; 30(4):764-772. [16]Chaudhry H,Kleinlugtenbelt YV,Mundi R,et al.Are volar locking plates superior to percutaneous k-wires for distal radius fractures? A meta-analysis.Clin Orthop. 2015;473(9):3017-3027.[17]Jantzen C,Cieslak LK,Barzanji AF,et al.Colles' fractures and osteoporosis--A new role for the Emergency Department. Injury. 2016; 47(4):930-933.[18]Sander AL,Leiblein M,Sommer K,et al.Epidemiology and treatment of distal radius fractures: current concept based on fractureseverity and not on Age. EurJ Trauma Emerg Surg.2018.doi: 10.1007/s00068-018-1023-7.[19]Arnold CM,Dal Bello-Haas VP,Farthing JP3,et al.Falls and Wrist Fracture: Relationship to Women's Functional Status after Age 50.Can J Aging. 2016;35(3):361-371.[20]任威,王小龙,赵建民,等.呼和浩特市60岁以上蒙古族人群桡骨远端骨折的调查研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2015,22(20):1863-1868.[21]刘松,李佳,韩志刚,李石伦,等.2010至2011年我国华北和华东地区老年Colles骨折患者的流行病学特征分析[J].中华老年骨科与康复电子杂志, 2018,4(3):180-183.[22]Blakeney WG.Stabilization and treatment of Colles' fractures in elderly patients.Clin Interv Aging.2010;5:337-344. [23]Sakai A,Oshige T,Zenke Y,et al.Association of bone mineraldensity with deformity of the distal radius in low?energy Colles'fractures in Japanese women above 50 years of age.J Hand Surg Am.2008; 33(6):820-826.[24]Wilcke MK,Hammarberg H,Adolphson PY.Epidemiology and changed surgical treatment methods for fractures of the distal radius: a registry analysis of 42,583 patients in Stockholm County, Sweden, 2004-2010. Acta Orthop. 2013;84(3):292-296.[25]Raittio L,Launonen A,Hevonkorpi T,et al.Comparison of volar-flexion, ulnar-deviation and functional position cast immobilization in the non-operative treatment of distal radius fracture in elderly patients: a pragmatic randomized controlled trial study protocol.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2017;18:401.[26]Jian-cai S.Treatment of Colles fracture with manipulative closed reduction and U-shaped gypsumfunctional fixation. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2016;29(1):18-20.[27]Sarmiento A,Latta LL.Colles'fractures:functional treatment in supination. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2014;81(3):197-202.[28]桂光明,曹波,张惠,等.石膏托和小夹板外固定对Colles骨折复位后短期位置丢失的影响[J].中医正骨,2016,28(4):19-21,24.[29]高勇军.手法复位石膏外固定治疗Colles骨折274例临床分析[J].实用医技杂志,2013,20(9):1003-1004.[30]罗公瑾,高亚东.手法复位石膏外固定腕关节不同位置治疗Colles骨折的疗效观察[J].临床合理用药杂志, 2012,5(6):106-107.[31]Gelberman RH,Szabo RM,Mortensen WW.Carpal tunnel pressures and wrist position in patients with colles' fractures.J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 1984;24(8):747-749. [32]Dyer G,Lozano-Calderon S,Gannon C,et al.Predictors of acute carpal tunnel syndrome associated with fracture of the distal radius.J Hand Surg. 2008;33(8):1309-1313.[33]袁世民,梁奇文,梁树禄,等.点牵引手法复位树脂绷带外固定治疗粉碎性Colles骨折60例[J].江西中医药,2016,47(7):35-37.[34]邢振龙,丘青中,李颖,等.改良手法复位树脂绷带外固定治疗Colles骨折75例临床观察[J].河北中医,2013,35(4):635-637.[35]Cazon A,Kelly S,Paterson AM,et al.Analysis and comparison of wrist splint designs using the finite element method: Multi-material three-dimensional printing compared to typical existing practice with thermoplastics.Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2017;231(9):881-897.[36]Davison PG1,Boudreau N,Burrows R,et al. Forearm-Based Ulnar Gutter versus Hand-Based Thermoplastic Splint for Pediatric Metacarpal Neck Fractures: A Blinded, Randomized Trial.Plast Reconstr Surg.2016; 137(3):908-916.[37]曹建,谢海燕,章长征.低温热塑板外固定治疗四肢骨折体会[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2014,12(14):1113.[38]曾池风,刘海燕,等.低温热塑板与普通石膏外固定治疗colles骨折的疗效比较[J].实用医学杂志,2009,25(11):1813-1814.[39]吴强,赖华兵,杨霖.低温板材外固定治疗桡骨远端伸直型骨折96例:与夹板外固定及石膏夹板超腕外固定的比较[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2010,14(42):7955-7958.[40]郭刚.两种外固定方法治疗Colles骨折的疗效对比分析[J].河南外科学杂志, 2013,19(1):29-30.[41]Al Khudairy A,Hirpara KM,Kelly IPConservative treatment of the distal radius fracture using thermoplastic splint: pilot study results.Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol.2013;23(6):647-650.[42]段宗耀,章汉平.低温热塑板联合接骨膏外敷治疗桡骨远端不稳定骨折临床观察[J].湖北中医杂志,2015,37(6):60-61.[43]杜竑磊.低温热塑板外固定术治疗老年Colles骨折的疗效分析[J].深圳中西医结合杂志,2015,25(1):126-127.[44]Kasapinova K,Kamiloski V.Pain and disability during six months in patients with a distal radius fracture.Prilozi. 2009;30(2):185-196. |
| [1] | Hu Kai, Qiao Xiaohong, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong, Qin Sihe. Treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures with cannulated screws and plates: a meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1465-1470. |
| [2] | Xu Feng, Kang Hui, Wei Tanjun, Xi Jintao. Biomechanical analysis of different fixation methods of pedicle screws for thoracolumbar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1313-1317. |
| [3] | Zhang Chong, Liu Zhiang, Yao Shuaihui, Gao Junsheng, Jiang Yan, Zhang Lu. Safety and effectiveness of topical application of tranexamic acid to reduce drainage of elderly femoral neck fractures after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1381-1386. |
| [4] | Chen Xinmin, Li Wenbiao, Xiong Kaikai, Xiong Xiaoyan, Zheng Liqin, Li Musheng, Zheng Yongze, Lin Ziling. Type A3.3 femoral intertrochanteric fracture with augmented proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in the elderly: finite element analysis of the optimal amount of bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1404-1409. |
| [5] | Du Xiupeng, Yang Zhaohui. Effect of degree of initial deformity of impacted femoral neck fractures under 65 years of age on femoral neck shortening [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1410-1416. |
| [6] | Zhang Chao, Lü Xin. Heterotopic ossification after acetabular fracture fixation: risk factors, prevention and treatment progress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1434-1439. |
| [7] | Zhou Jihui, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao. Multiple problems in the selection of implants for patellar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1440-1445. |
| [8] | Wang Debin, Bi Zhenggang. Related problems in anatomy mechanics, injury characteristics, fixed repair and three-dimensional technology application for olecranon fracture-dislocations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1446-1451. |
| [9] | Xu Yulin, Shen Shi, Zhuo Naiqiang, Yang Huilin, Yang Chao, Li Yang, Zhao Heng, Zhao Lu. Biomechanical comparison of three different plate fixation methods for acetabular posterior column fractures in standing and sitting positions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 826-830. |
| [10] | Cai Qunbin, Zou Xia, Hu Jiantao, Chen Xinmin, Zheng Liqin, Huang Peizhen, Lin Ziling, Jiang Ziwei. Relationship between tip-apex distance and stability of intertrochanteric femoral fractures with proximal femoral anti-rotation nail: a finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 831-836. |
| [11] | He Li, Tian Wei, Xu Song, Zhao Xiaoyu, Miao Jun, Jia Jian. Factors influencing the efficacy of lumbopelvic internal fixation in the treatment of traumatic spinopelvic dissociation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 884-889. |
| [12] | Yang Weiqiang, Ding Tong, Yang Weike, Jiang Zhengang. Combined variable stress plate internal fixation affects changes of bone histiocyte function and bone mineral density at the fractured end of goat femur [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 890-894. |
| [13] | Zhang Lei, Ma Li, Fu Shijie, Zhou Xin, Yu Lin, Guo Xiaoguang. Arthroscopic treatment of greater tuberosity avulsion fractures with anterior shoulder dislocation using the double-row suture anchor technique [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 895-900. |
| [14] | Zhang Jing, Wang Bin, Lü Xin. Application of anatomic intramedullary nail in tubular bone fractures of limbs: stronger holding force and anti-rotation ability [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 917-922. |
| [15] | Kong Lingbao, Lü Xin. Effect of implant selection and approach on support in the operation of posterolateral tibial plateau fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 942-947. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||